How to Create the Bar Bending Schedule Of Slab
Create the Bar Bending Schedule Of Slab

How to Create the Bar Bending Schedule Of Slab
A Bar Bending Schedule is the comprehensive list that presents the details of reinforcement bars in a tabular format. It includes information such as the shape of the bending with accompanying sketches, length of each bar, total weight, and the overall length of the bars. How to Create the Bar Bending Schedule Of Slab.
The process of bar bending involves cutting & shaping reinforcement steel bars according to the desired shape specified in the structural drawing provided by the structural engineer. This process is carried out for the various structural elements such as footings, columns, beams, slabs, and more. How to Create the Bar Bending Schedule Of Slab.

When working with reinforced cement concrete, it is customary to maintain a schedule of bars. The Bar Bending Schedule serves as a valuable tool in understanding the requirements for different sizes of the bars and their respective lengths. This allows for proper arrangement and bending of the bars during the construction phase. By creating and adhering to a bar bending schedule, we are able to stay well-informed and organized throughout the construction process. How to Create the Bar Bending Schedule Of Slab.
- The shape of the bending along with its sketch.
- Number of the sets or number of bars of each set.
- Length of the each and the total length of a running meter.
- The total weight of the bars.
- Size and Type of the Bars.
This article will primarily concentrate on the procedure of the bar bending schedule, the steps involved in its creation, and the key benefits associated with its development.
Types of the slabs used in the Bar Bending schedule.
Slabs can be classified into 2 types
- 1 way Slab
- 2 -way slab
1 way Slab
In the 1 way slabs the main bars are provided in the shorter direction whereas distribution bars are provided in longer direction
Read More
Basics Of Land Surveying
Derivation of formula to set out the curves by the method of ordinates from a long chord
Estimation of the Material for Concrete
Components of Road Structure
2 -way Slab
In 2 -way slabs, the main bar are provided in the both directions.
Estimating Bar bending schedule of the 1 way slab.
For the perfect bar bending schedule in 1 way slab, we should consider following example
Length of slab = 5000 mm
Width of the slab = 2000 mm
Main Bar = 12mm @ 150 mm/cc
Ly/Lx = Longer span /Shorter span
=5000/2000
=2.5 > Two
Distribution Bar = Eight mm @ 150 mm/cc
Clear Cover (Top and the Bottom) = twenty five mm
Thickness of the slab =150 mm
Development Length = 40 d
Where d is diameter of the Bar.
To calculate the bar bending schedule of 1 -way slab.
No 1 =
Calculate no of the bars
Calculate no of the bars required for main bars & distribution bars
No of the bars = Length of the Slab/ spacing + One
No of the main bars = Lx/spacing + One
=5000/150
= 34
Then we have to calculate no of the distribution bars
= Ly/Spacing + One
=2000/150 + One
=14
No 2 =
Calculate cutting length of the main bars & distribution bars
Cutting length of the main bar
= clear span of the slab + (Two x development length) + inclined length – (bend length)
The Clear Span of the Slab = 2000 mm
The Development Length = 40 d
Inclined length = 0.42 d
One d is for every 45º bend
Where d = diameter of the Bar
Now let us calculate D
D = The Thickness of the slab – Both side clear cover (Top and the Bottom) – diameter of the bar.
= 150 – (25 + 25) – Twelve
= 88 mm
Length of the main bar
=Ly +2Ld + (One x 0.42d) – (1d x Four)
= 2000 + (Two x 40 x 12) + (Two x 0.42 x 88) – (One x 12 x 4)
=2838 mm
=2.838 m
The Weight of the main bars = d2 x L/162 X 34
=122 x 2.838/162
=86 kg
Read More
What is contour interval and Uses of contour maps in surveying
how to Calculate the height of an object using With theodolite
Concrete Slump Test workability Procedure and result
What is Best Practice in the Construction
Types of Maps in the Drone Mapping
Length of the Distribution Bar.
The Clean span of the slab + Two x development length
= Lx + Two Ld
= 5000 +Two x 40 x Eight
=5640 mm
=5.64 m
Weight of the distribution bars
= d2 x L/162 x14
=82 x 5.64/162 x 14
= 31 kg
No 3 =
Calculate the top bar which is the provided at the top of the critical length (L/four) area
No of the Top Bars = {(Ly/4)/spacing+1}x Two
= {(2000/4)/150+1} x Two = Nine
Length of the extra bar = Ly – 2x Ly/4 +Two x 100
{Here Two x 100 is for the both side Lapping of 100 mm for the extra bar}
= 2000 – (Two x 2000/4) +200
=1200 mm
=1.2 m
The Weight of the Extra Bar = d2 x L/162 x Nine
= 82 x 1.2/162 x Nine
=4.266 kg
Bar Bending Schedule Of the 2 Way Slab
So i know, Longer span/Shorter span = Ly/Lx
=5000/3000
=1.66 < Two
It is the 2 -way slab
Given,
The Length of the Longer Span = 5000 mm
The Length of the Shorter Span = 3000 mm
Main Bar = 12 mm @150 mm/cc
Clear Cover (Top and Bottom) = twenty five mm
Thickness of the slab = 20 mm
Development Length = 40 d
Where d is the diameter of bar
Step By Step Method is To calculate the BBS of the 2 way slab
Read More
Thumb rule for Civil Engineers
What Is The RCC Concrete And Properties of RCC Concrete
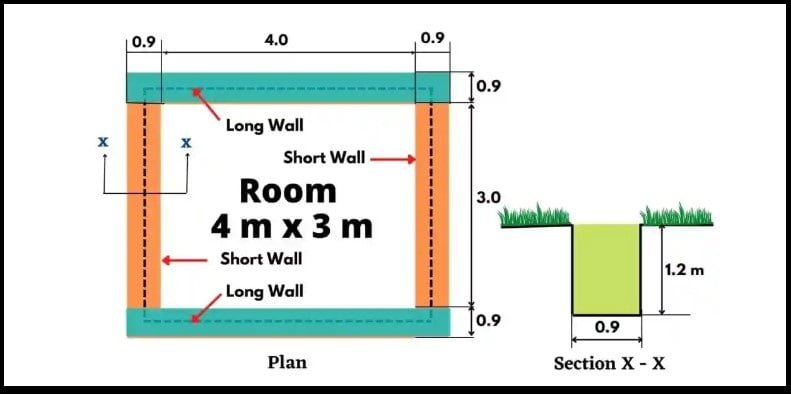
What is the Long Wall Short Wall Method
Step No 1: For section A – A
Calculate number of the bars required for main bars and the distribution bar
No of the Bars = Length of slab/spacing +One
Total no of the bars = Ly/150 +One
=4000/150+ One
=27
No of the main bars =14
No of the distribution bars =13
Step No 2:
Calculate cutting length of the main bars and distribution bars
Cutting length of the Main Bar = Clear span of the slab +(Two x development length) + (inclined length) – (Bend length)
Clear Span of the slab= 5000 mm
Development Length = Ld°°
Ld = 40d
Inclined length = 0.42d
One d is for every 45° bend
Where d is the diameter of bar
Now Calculate D
D = Thickness of the slab – both side clear cover (top and the bottom) – diameter of the bar.
200 – (25 +25) – twelve = 138 mm
Length of the Main bar = Lx +(Two x Ld) + (2 x 0.42d) – (1d x four)
= 5000 +(Two x 40 x 12) + (Two x 0.42 x 138) – (One x 12 x4)
=2838 mm
=6.02 m
For 14 bars of total length
=6.02 x 14
= 84.28 m
Weight of the main bars= d2 x L/162
= 122 x 84.28/162
=75 kg
Cutting Length of the Distribution Bar
= clear span of the slab + Two x development length
= Lx +Two Ld
= 5000 +Two x 40 x Eight
=5640 mm
=5.64 m
Total Length of the Distribution Bar
=5.64 x 13
= 73.32
Weight of the Distribution Bars
=d2 x L/162
= 82 x 73.32/162
=29 kgs
Step No 3:
Calculate Top Bar which is provided at the top of the critical length(L/four) Area
No. Of Extra Bars ={(Ly/4)/spacing +1}x Two
={(4000/4)/150 +One} x Two =16
Length of the Extra Bar = Lx – Two x Lx/4+Two x100 [ here Two x100 is for both side lapping of 100 mm of the extra bar]
=5000 – (Two x 5000/4) + 200
=2800 mm
=2.7 mm
Total Length Of the Extra Bar
= 2.7 x Sixteen
= 43.8
Weight of the Extra Bar = d2 x L/162
= 82 x 43.2/162
=17 Kg
Step No 1 For Section B-B
Calculate number of the bars required for main bars and the distribution bar
Total No. of the Bars = Length of Slab/Spacing + One
Total No. of the Bars = Lx/150 + One
=5000/150 + One
=35
No. Of the Main Bars = 18
No. Of the Distribution Bars = 17
Calculate The Cutting Length of the Main Bars.
Cutting length of the Main Bar = Clear span of the slab +(Two x development length) + (inclined length) – (Bend length)
Clear Span of the Slab = 4000mm
Development length = Ld = 40d
Inclined Length = 0.42d
One d is for every 45° bend
Where d = Diameter of bar
Now let us calculate d
d = Thickness of the Slab – Both Side Clear Cover – Diameter of the Bar
= 200 – (25+25) – twelve
=138 mm
Cutting Length Of the Main Bar
= Ly + 2 x Ld
= 4000 + 2 x 40 x Eight
=4640 mm
= 4.64 m
Total Length Of the Distribution Bar
=4.64 x Seventeen
= 78.88
Weight of the Distribution Bars
= d2 x L/162
= 82 x 78.88/162
=31 kg
Read More
Step No 3 :
Calculate No of the Extra Bars
No. Of the Extra Bars = {( Lx /4)/spacing +One } x Two
={(5000/4)150 + One} x 2 = Nine
Length of Extra Bar = Ly -(Two x -Ly/4) + (Two x 100) [here Two x 100 is for both side lapping of 100 mm for the extra bar]
= 4000 – (Two x 4000/4) + 200
=2200 mm
=2.2 m
Total Length of the Extra Bar
=2.2 x Nine
=19.8 m
Weight of the Extra Bar
= d2 x L/162
=82 x 19.8/162
=Eight kg
Thus in these easy step-to-step methods, 1 can create BBS.
Advantages of the (BBS) Bar Bending Schedule.
The following are the main advantages of the BBS
- It helps in the stock management at the site
- It helps in auditing of the reinforcement and provides the check on theft.
3) 1 can estimate the steel qty through BBS.
In conclusion,
it is hoped that this article has provided valuable information, enabling individuals to accurately determine the Bar Bending Schedule by following these straightforward instructions.




2 Comments