Deflection angle in Surveying
Definition
A deflection angle is an angle which is the survey line makes with the prolongation of the proceeding line. A deflection angle vary from 00 to 180 but never more than 180. The deflection angle measured clockwise direction from the prolonged survey line is known as the right deflection angle. What is Deflection Angle in Surveying

In surveying, the term “deflection angle” refers to the angle by which a line or a segment deviates from a reference direction or a baseline. Understanding deflection angles is crucial for accurately determining the alignment of features, plotting curves, and ensuring the precision of survey measurements. Here’s a detailed explanation of deflection angles and their importance in surveying:
1. Definition and Concept
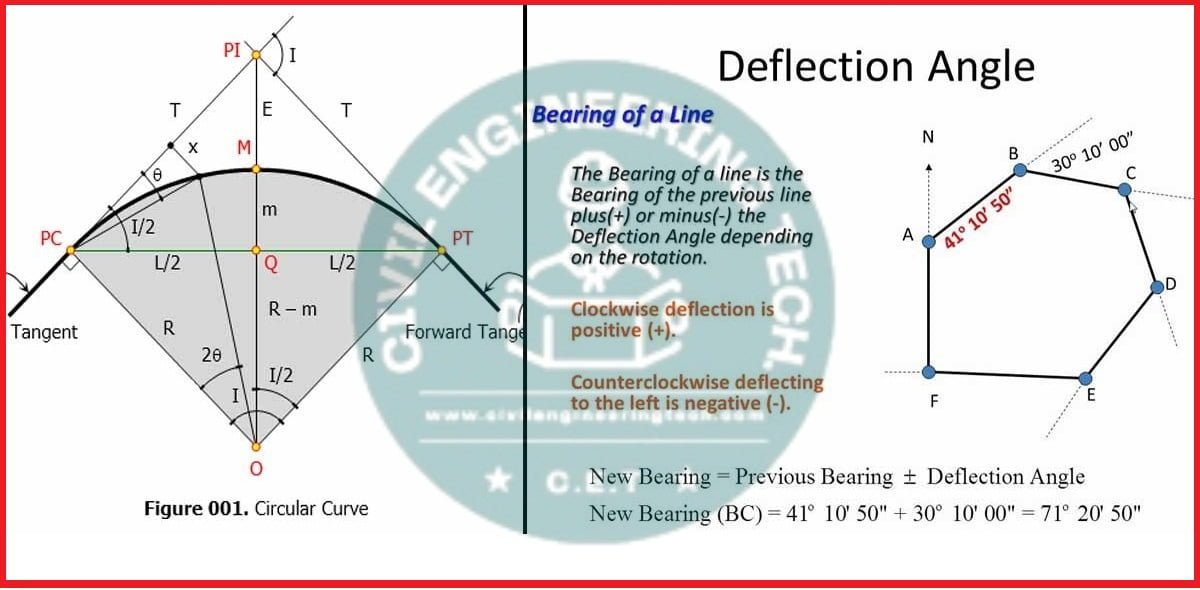
Deflection Angle
The deflection angle is the angle between the direction of a baseline (or a reference line) and a survey line (or an alignment line) at a specific point. It indicates how much the survey line deviates from the baseline.
In practical terms, if you have a straight reference line and a survey line that turns at a certain point, the deflection angle is the angle between these two lines at that turning point.
2. Importance in Surveying
Alignment of Roads and Highways
In road construction, deflection angles are used to ensure that the alignment of roads follows the designed path. Accurate deflection measurements are critical for maintaining the intended curvature and direction of the road.
Curve Setting in Engineering
When setting out curves in construction, such as for railways or highways, the deflection angle helps in determining the exact path of the curve. Proper calculation and measurement of deflection angles ensure smooth transitions and accurate curves.
Learn More
What Is The Benefits Of Civil Engineering Insurance
How to install the HDPE line in paving concrete
Method Of Statement for Survey Works
Land Subdivision and Property Boundaries
Deflection angles are used to establish and verify property boundaries and land subdivisions. Accurate measurement of these angles helps in maintaining legal and physical boundaries as per the land survey plans.
Mapping and Plotting
In topographic mapping, deflection angles help in plotting the features of the land accurately. They are essential for translating the three-dimensional characteristics of the land onto a two-dimensional map.
3. Measurement and Calculation
Field Measurement
Deflection angles can be measured using various surveying instruments, such as:
Theodolites:
These instruments are used to measure horizontal and vertical angles, including deflection angles, with high precision.
Total Stations:
Modern total stations combine electronic distance measurement with angular measurement to determine deflection angles and other survey parameters.
Calculation of Deflection Angles
The deflection angle is calculated based on the observed angles and the known reference lines. The calculation often involves:
- Measuring the angle between the reference line and the survey line at a point.
- Using trigonometric formulas to determine the deviation from the baseline.
4. Types of Deflection Angles
Right Deflection Angle
When the survey line turns to the right from the baseline, the deflection angle is considered positive and is called a right deflection angle.
Left Deflection Angle
When the survey line turns to the left from the baseline, the deflection angle is considered negative and is referred to as a left deflection angle.
5. Applications and Examples
Road Design
In road design, deflection angles are used to create smooth curves and turns. For instance, if a road is designed to curve at a specific point, the deflection angle helps in aligning the road correctly and ensuring that the curve meets safety and design standards.
Railway Alignment
For railways, deflection angles are used to set the correct curvature of tracks, ensuring smooth transitions between straight sections and curves. This is essential for maintaining train safety and comfort.
Learn More
How To Calculate the Quantity Of Concrete Volume Of Staircase
Basics Of Land Surveying
Derivation of formula to set out the curves by the method of ordinates from a long chord
Surveying for Construction Projects
In construction projects, such as building foundations or pipelines, deflection angles are used to ensure that the construction aligns with the planned design. Accurate deflection angle measurement prevents misalignment and construction errors.
Property Boundaries
When subdividing land or establishing property boundaries, deflection angles help in ensuring that the boundaries are accurately marked and conform to legal requirements.
6. Challenges and Considerations
Accuracy of Measurement
Precise measurement of deflection angles is critical for the accuracy of the entire survey. Any errors in measuring deflection angles can lead to significant deviations in the final layout.
Instrument Calibration
Surveying instruments used to measure deflection angles must be properly calibrated to ensure accurate results. Regular maintenance and calibration are essential for reliable measurements.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as weather conditions and terrain, can impact the accuracy of deflection angle measurements. Surveyors need to account for these factors to ensure precision.
Other Post
Concrete Slump Test workability Procedure and result
What is contour interval and Uses of contour maps in surveying
Estimation of the Material for Concrete
What is Difference between Plinth Beam and Tie Beam





