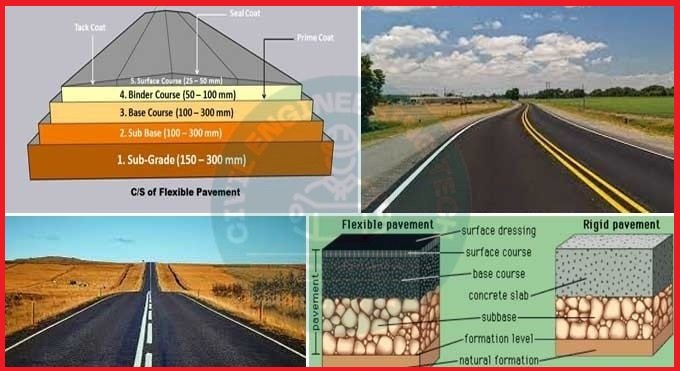
Components of Road Structure
This article aims to provide an explanation of the various components and structure of roads, as well as their composition. By reading this article, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of the different elements that make up road structures. I will strive to present the information in a simplified manner for easy comprehension. Components of Road Structure.

There are few components of the road structure which are going to be discuss below which are as follows:
CARRIAGEWAY.
FORMATION WIDTH.
KERB.
ROAD MARGIN.
MEDIANS.
CAMBER.
RIGHT OF WAY.
(1) Carriage Way
The Carriageway refers to the width of the road where traffic flows without any hindrance. It typically includes traffic lines, and the carriageway’s width is determined by the number of traffic lines. Traffic lines are designated areas where vehicles can move without obstruction. Different countries have their own regulations regarding the carriageway width, such as 2.44m for a single lane road in some countries, and 3.75m for a two-lane road in others.
(2) Formation Width.
The formation width of the road is sum of the carriageway, shoulders & separators (if there is any).
(3) Kerb.
Kerbs serve as the boundary line made of stone or concrete blocks that separate the carriageway from the footpath. There are various types of kerbs with different heights, including low or mountable kerbs, semi-barrier kerbs, barrier kerbs, and submerged kerbs. Low kerbs help traffic stay in line and separate the shoulder from the road, with a height of ten cm (four inches).
Learn More
What Is The RCC Concrete And Properties of RCC Concrete
What is the Long Wall Short Wall Method
What is the Differences between Pillar and Column
Semi-barrier kerbs have a height of fifteen cm (six inches), while barrier kerbs are twenty cm (eight inches) high and are placed in areas with high pedestrian traffic. Submerged kerbs are used in rural roads to provide stability to the road pavement.
(4) Road Margin.
The sections of the road that are not part of the carriageway are commonly referred to as the road margin. It encompasses various components or elements of the road, which are listed below.
Shoulders.
Bus bays.
Parking lines.
Sidewalks or footpaths.
Service roads.
Cycle track.
Guard rails.
Drive way.
Frontage roads.
(1) Shoulders.
The shoulders are a component of the road width excluding the carriage way. Positioned next to the carriageway, they serve as an emergency lane during peak traffic hours or for vehicle repairs, and can also allow for road expansion in the future. The width of the shoulders typically ranges from 2.5 m to 4.6 m.
(2) Bus Bays.
Bus bays or bus stops are located on the side of the road where buses can safely halt to board or disembark passengers without causing any disruption to the flow of traffic. These designated areas are positioned at a minimum distance of 75 meters (250 feet) away from road intersections.
(3) Parking Lines.
Parking is typically available on the side of urban roads, with parallel parking being the preferred option to avoid disrupting traffic flow. The width of the parking space is three meters (10 feet).
(4) Sidewalks or Footpath.
The term “Sidewalks” and “footpath” are synonymous. In situations where there is a high volume of traffic and pedestrians, a designated paved area is allocated to ensure the safety of pedestrians and prevent accidents
(5) Service Road.
Service roads run parallel to the main road and also link up with the main highway and expressway. They are distinct from the main road and connect to the highway at specific locations. Their purpose is to ensure smooth traffic flow without disruptions.
(6) Cycle Track.
Cycle lanes are installed in regions with significant bicycle traffic, with the track’s width varying from two to three meters, or alternatively, six to ten feet
(7) Guard Rails.
Guard rails are typically installed along the edge of road. They are installed when the drop is greater than three meters (ten feet). Their primary function is to prevent vehicles from veering off the road and to minimize the risk of serious accidents. Guard rails come in various types and shapes, such as steel, concrete, or stone. They are often painted white or yellow to enhance visibility.
(5) Medians.
The Medians are designed to separate traffic and prevent collisions between vehicles traveling in opposite directions. Their primary function is to enhance of road safety
(6) Camber.
The Camber, also known as cross slope, is strategically placed in the center of the road or carriageway to facilitate the drainage of rainwater from the road surface. Its primary function is to safeguard the subgrade of the road by ensuring that water does not seep through.
Learn More
Civil Engineering Interview Questions and Answers
Calculation of Bricks and Blocks in the Wall
Civil Engineering Basic Field Knowledge
This, in turn, allows the road to dry quickly, reducing the risk of accidents caused by slippery surfaces. The height of the camber is determined by the type of road material and the amount of rainfall in the area. The degree of camber typically ranges from one to 25 or one to 50.
(7) Right of Way.
The total land required for road construction is known as the right of way. This encompasses the carriageway, footpath, and any potential future extensions. The extent of the right of way is determined by the significance of the road and its potential for future expansion.
(8) Drive Way.
The driveway connects to the highway, providing access to various commercial establishments such as gas stations, filling stations, and petrol stations, among others.
(9) Frontage Roads.
The Frontage Roads is the constructed to give acquire properties along an essential highway. It may be run parallel to the highway and segregated by separators.
Thank You For Reading This Important Information. Get Benefits And Share With New Commers.




Excellent work 😊
very informative information.